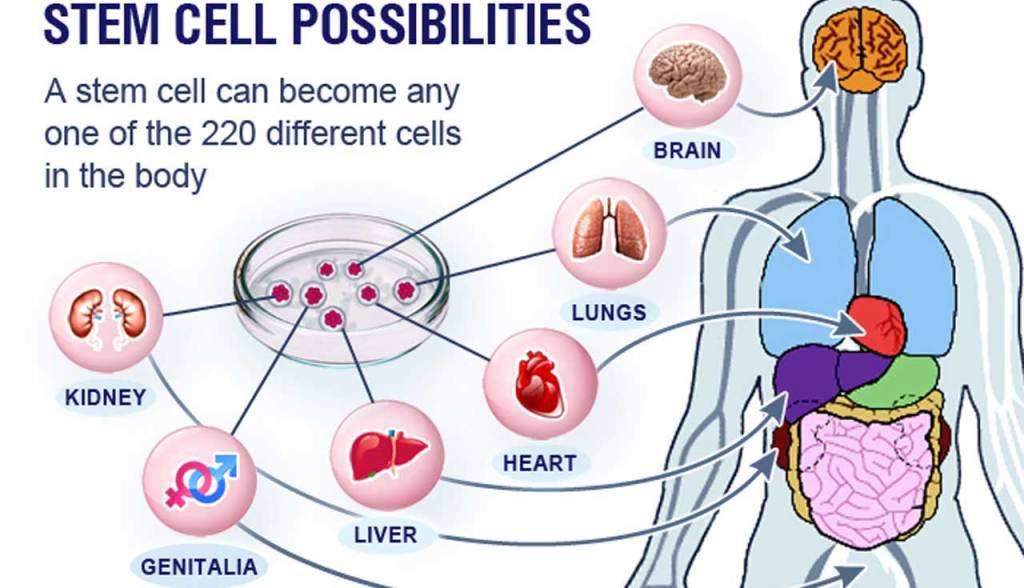
Stem cells help to eliminate the cause of disorders leading to a reduction in symptoms or a full recovery, depending on the initial condition, for (mostly) autoimmune disorders and/or diseases associated with tissue damage.
There is a large percentage of cases with a variety of diseases that have experienced health improvements. Applying only stem cells for some cases may be not enough. Cell therapy works more effectively when combined with other therapeutic methods that help decrease inflammation, restore mobility, activate the tissue repair process.
We’ve seen various levels of recovery after treating the following diseases (not a full list):
Neurological disorders
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Parkinson’s disease
- Dementia
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Post-stroke condition
- Injuries of CNS
- Lyme disease
Endocrine diseases
- Diabetes type 2
- Diabetic foot
- Erectile dysfunction
- Obesity
Musculoskeletal disorders
- Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis
- Sports-related injuries complications
- Athletic performance improvement
Digestive System Diseases
- Crohn’s disease
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Peptic ulcer disease
- Chronic pancreatitis
Respiratory diseases
- COPD
- Asthma
- Allergic rhinitis
- Sarcoidosis
Rheumatic diseases
- Systemic scleroderma
- Dermatomyositis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Lupus
- Vasculitides
It is important to understand that stem cells are not a guaranteed cure for every disease.The patient may be denied stem cell procedures for various reasons. The effectiveness of the therapy for a particular disease depends on multiple factors: duration of the illness, age of the patient, the existence of chronic conditions, hereditary predisposition, lifestyle, etc.







You must be logged in to post a comment.