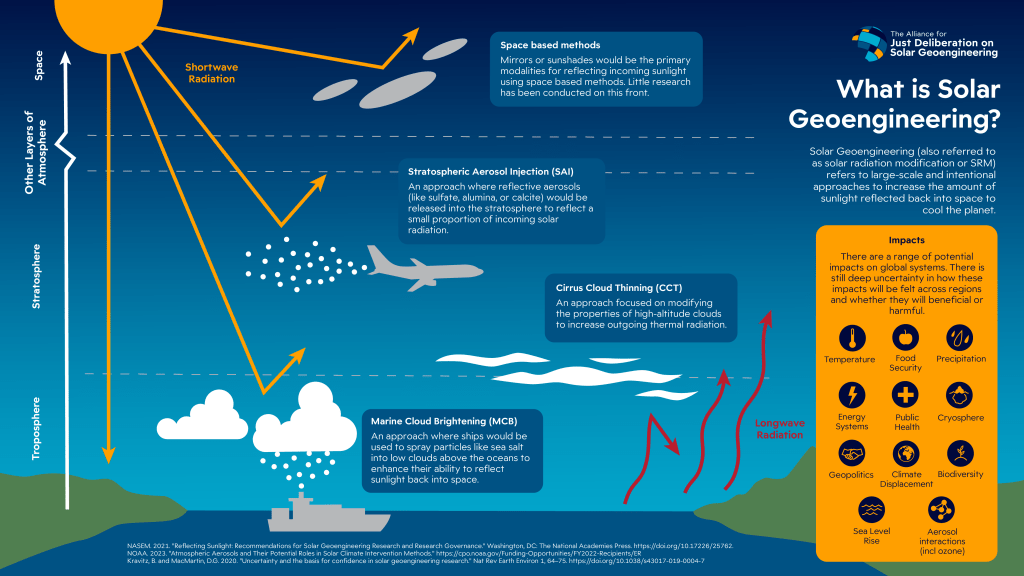
UK scientists, backed by a £50 million government-funded programmed led by the Advanced Research and Invention Agency (Aria), plan to launch small-scale outdoor geoengineering experiments aimed at evaluating technologies that could temporarily reduce global warming. The experiments will primarily investigate methods of solar radiation management (SRM), such as:
- Launching reflective particles into the atmosphere.
- Using seawater sprays to enhance cloud reflectivity.
🚧 Why the Experiments?
- To provide critical real-world data about whether these geoengineering technologies could effectively and safely cool the Earth temporarily.
- To assess potential unintended consequences, like shifts in rainfall patterns that could impact global food security.
- To understand the feasibility of rapidly deploying these technologies as an emergency measure to avoid climate “tipping points” (e.g., collapse of ice sheets, critical ocean currents).
⚠️ Controversy and Concerns
- Environmental Risks: Critics argue these methods might cause significant unforeseen environmental consequences, including disrupted rainfall.
- Diversion from Emissions Cuts: Some scientists label SRM as a “dangerous distraction,” fearing it might reduce global efforts to tackle fossil fuel emissions directly.
- Ethical and Geopolitical Issues: There’s no international regulatory framework governing geoengineering, raising concerns about potential conflicts among nations.
🔬 Project Approach and Safeguards
- The experiments will be small-scale, rigorously assessed, and exclude toxic substances.
- An environmental impact assessment will precede any outdoor experiments.
- Local communities will be involved and consulted.
🌍 Broader Context
- The UK is becoming one of the world’s leading funders of geoengineering research, partly due to reductions in similar funding from the US.
- Another £10 million UK programme, led by the National Environment Research Council (NERC), will rely on computer models and natural analogues instead of outdoor experiments.
🌡️ Scientists’ Perspectives
- Proponents argue that researching SRM is essential due to the urgent need for rapid climate interventions.
- Critics describe SRM as inadequate or misguided, equating it to treating serious illnesses superficially rather than addressing underlying causes.







You must be logged in to post a comment.