By Iqra Sharjeel

Clomid (Clomiphene Citrate): A Comprehensive Overview
Clomid, the brand name for clomiphene citrate, is a widely used oral medication in reproductive medicine. As a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM), it plays a pivotal role in treating certain types of infertility in both women and men.This report delves into Clomid’s mechanisms, applications, efficacy, side effects, dosage guidelines, comparisons with other fertility drugs, and patient experiences.
1. Mechanism of Action
Clomid functions by modulating estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, leading to an increase in the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). This, in turn, stimulates the anterior pituitary gland to secrete higher levels of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), promoting ovulation in women and enhancing testosterone production in men .
2. Use in Female Infertility
Indications
Clomid is primarily prescribed for women experiencing anovulation or oligo-ovulation, conditions often associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). It is also utilized in cases of unexplained infertility and as an adjunct in assisted reproductive technologies.
Effectiveness
Clinical studies have demonstrated that Clomid induces ovulation in approximately 70-80% of women, with conception rates varying based on underlying conditions. For instance, a decade-long study involving 428 women reported an ovulation rate of 85.3% and a conception rate of 42.8% .
Treatment Regimens
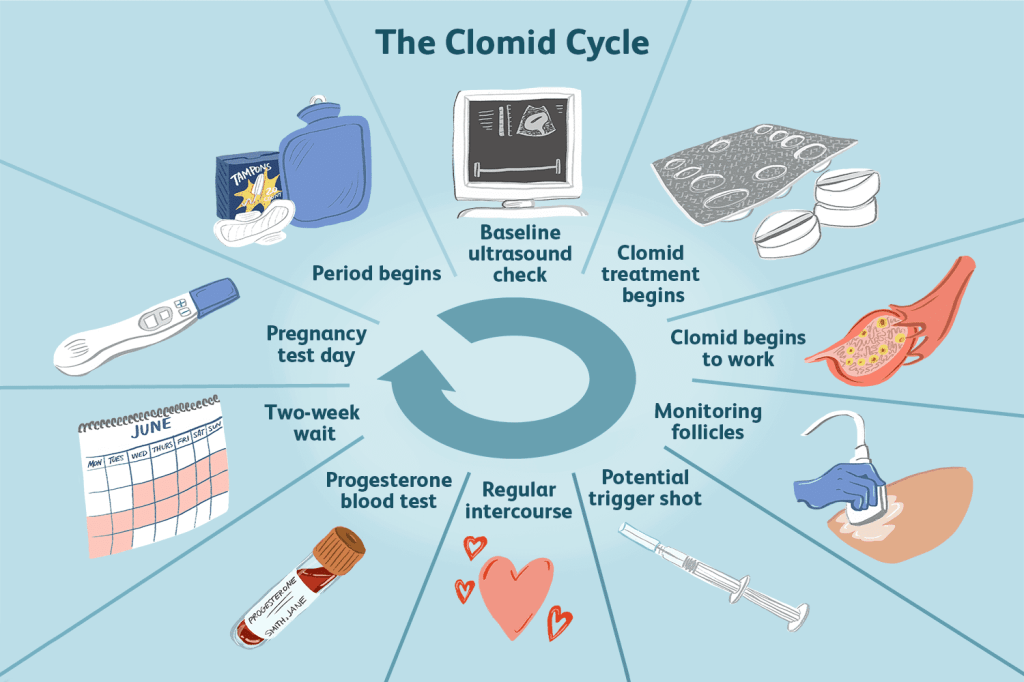
The standard protocol involves administering 50 mg of Clomid daily for five days, typically starting on the fifth day of the menstrual cycle. If ovulation does not occur, the dosage may be increased in subsequent cycles, not exceeding 150 mg per day .
3. Use in Male Infertility and Low Testosterone Treatment
Mechanism and Outcomes
In men, Clomid acts by increasing endogenous testosterone levels through stimulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. This can lead to improvements in sperm concentration and motility, making it a viable treatment for certain cases of male infertility .PubMed
Off-Label Considerations
While not FDA-approved for male infertility, Clomid is often used off-label for this purpose. It offers an alternative to testosterone replacement therapy, particularly for men desiring to maintain fertility.
4. Dosage Guidelines and Treatment Plans
Women
- Initial Dose: 50 mg daily for five days.
- Adjustment: If ovulation does not occur, the dose may be increased by 50 mg increments in subsequent cycles, up to a maximum of 150 mg daily.
- Duration: Treatment is typically limited to six cycles to minimize risks.RxList+4PubMed Central+4Medscape+4
Men
- Dosage: Common regimens include 25 mg every other day or 25 mg daily.
- Monitoring: Regular assessments of testosterone levels and semen analysis are recommended to evaluate efficacy and adjust dosing.
5. Success Rates and Clinical Studies
- Female Infertility: Clomid induces ovulation in up to 80% of women, with pregnancy rates ranging from 30-40% over six cycles .
- Male Infertility: Studies have shown significant improvements in sperm parameters, with some men achieving natural conception following treatment .auajournals.org
6. Side Effects and Risks
Common Side Effects
- Hot flashes
- Bloating
- Mood swings
- Breast tenderness
- Nausea
- Headaches
Serious Risks
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): A rare but serious condition characterized by enlarged ovaries and fluid accumulation.
- Visual Disturbances: Including blurred vision and scotomas; typically reversible upon discontinuation.
- Multiple Pregnancies: Increased risk of twins or higher-order multiples.
Long-Term Risks
Some studies have suggested a potential link between prolonged Clomid use and increased risk of ovarian cancer, though findings are inconclusive. It is generally recommended to limit Clomid use to six cycles .ParentsWikipedia
7. Comparison with Other Fertility Drugs
Letrozole (Femara)
- Mechanism: Aromatase inhibitor that reduces estrogen production, leading to increased FSH release.
- Efficacy: Studies indicate higher ovulation and live birth rates compared to Clomid, particularly in women with PCOS .
- Side Effects: Generally fewer and less severe than Clomid; lower risk of multiple pregnancies.Inito Blog+1the Lucky Egg+1Parents+1Parents+1
Gonadotropins
- Mechanism: Injectable hormones (FSH and LH) that directly stimulate the ovaries.
- Efficacy: Higher pregnancy rates but increased risk of OHSS and multiple gestations.
- Cost and Monitoring: More expensive and require close monitoring via ultrasound and blood tests.
8. Patient Experiences and Case Studies
Many patients report positive experiences with Clomid, citing its ease of use and effectiveness in inducing ovulation.However, some have experienced side effects such as mood swings and visual disturbances. In rare cases, Clomid has been associated with psychiatric symptoms, including mood changes and, in isolated instances, suicidal ideation.Advanced Fertility Center of Chicago™
Conclusion
Clomid remains a cornerstone in the treatment of certain types of infertility due to its efficacy, oral administration, and cost-effectiveness. While it offers significant benefits, it is essential to consider potential side effects and risks. Alternative treatments like letrozole may be more suitable for specific populations, such as women with PCOS. As with all medical treatments, individualized care and close monitoring by healthcare professionals are paramount to achieving optimal outcomes.







You must be logged in to post a comment.